SWOT Analysis: Identifying Strengths and Weaknesses
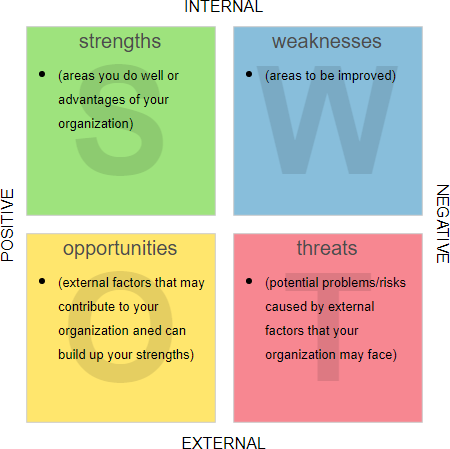
When it comes to making informed business decisions, understanding the strengths and weaknesses of your organization is crucial. A valuable tool that can aid in this process is the SWOT analysis. SWOT, which stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, provides a comprehensive overview of your company’s internal and external factors, allowing you to identify areas for improvement and capitalize on opportunities.
The Importance of SWOT Analysis
Effective strategic planning requires a deep understanding of the organization’s current position and its potential futures. A SWOT analysis offers a structured framework to evaluate these aspects critically. By conducting this analysis, you gain valuable insights into your company’s strengths and weaknesses while identifying potential opportunities and threats that can impact your success.
Identifying Strengths
The first step in conducting a SWOT analysis is identifying your organization’s strengths. These are the internal advantages or core competencies that give your business a competitive edge. Examples of strengths might include a strong brand reputation, loyal customer base, innovative products or services, leading technology, experienced workforce, or efficient processes.
To identify your strengths, consider what sets your company apart from competitors, what positive feedback you receive from customers or clients, and any resources you possess that contribute to your organization’s success. Once you have a clear understanding of your strengths, you can leverage them to maximize opportunities and counterbalance your weaknesses.
Recognizing Weaknesses
Contrary to strengths, weaknesses are internal factors that hinder your organization’s performance or prevent it from achieving its objectives. It is vital to identify these weaknesses to formulate strategies aimed at overcoming them. Weaknesses can be anything from outdated technology, lack of trained staff, limited financial resources, weak brand image, poor customer service, or inefficient operations.
When assessing weaknesses, it is essential to be honest and objective. Consider feedback from stakeholders, conduct internal audits, and evaluate any recurring issues or complaints. Identifying your weaknesses allows you to address them head-on, improving your overall performance and competitiveness.
Exploring Opportunities
Opportunities refer to external factors that have the potential to positively impact your organization. These may arise from market trends, technological advancements, changes in consumer behavior, emerging markets, or new business partnerships. By recognizing opportunities, you can adjust your strategies to capitalize on them, driving growth and innovation.
When exploring opportunities, it is essential to conduct market research, monitor industry trends, and stay updated with potential changes in legislation or market conditions. By staying proactive and receptive to change, you can seize opportunities before your competitors and gain a significant advantage.
Understanding Threats
Threats are external factors that have the potential to harm your business operations and performance. These may include increased competition, economic recessions, changing consumer preferences, disruptive technologies, or regulatory changes. Recognizing threats early on allows you to develop contingency plans and safeguards to mitigate their impact.
Stay vigilant by regularly monitoring the competitive landscape, researching industry trends, and assessing potential risks associated with your business. By identifying threats, you can proactively address them, minimizing the negative impact on your organization and maximizing your chances of success.
Implementing SWOT Analysis Results
Once you have completed your SWOT analysis and gained a comprehensive understanding of your organization’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, it is crucial to transform this knowledge into actionable strategies. Consider the following steps:
Build on strengths: Capitalize on your organization’s strengths by leveraging them to pursue new opportunities and gain a competitive advantage.
Address weaknesses: Develop strategies to mitigate weaknesses, such as investing in staff training, adopting new technologies, or improving processes.
Seize opportunities: Adjust your business strategies to capitalize on identified opportunities, whether it’s entering new markets or developing innovative products or services.
Minimize threats: Implement contingency plans to mitigate potential risks and ensure your organization is prepared to handle any challenges that may arise.
By implementing the insights gained from the SWOT analysis, you set yourself up for success, enabling your organization to adapt to changing environments, make informed decisions, and maintain a competitive edge.
Conclusion
A SWOT analysis is a powerful tool that allows organizations to gain a comprehensive understanding of their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. By carefully evaluating these internal and external factors, businesses can develop strategies to build on their strengths, address weaknesses, seize opportunities, and minimize threats. Implementing the insights gained from a SWOT analysis enables organizations to make informed decisions and stay ahead in a continually evolving business landscape.